A Layman’s Guide to NHCX
5 Dec 2023

Imagine a world where your healthcare and insurance data flow smoothly, securely, and without any hitches — that’s what the National Health Claims Exchange (NHCX) under the umbrella of the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) aims to create. It’s like an internet network, but for health claims, connecting different parties in healthcare — like hospitals, insurance companies, and patients — and allowing them to send and receive information about health insurance claims efficiently.
What is it for?
NHCX is built with multiple objectives to reform healthcare administration:
➡️ Standardizing Claims Processing
Creating a uniform, rule-based mechanism to reduce operational costs and build trust among stakeholders.
➡️ Fostering Insurance Innovations
Enabling the development of new rules and processes to enhance claim adjudication and prevent fraud.
➡️ Broadening Claims Coverage
Incorporating various types of healthcare expenses, like outpatient bills and pharmacy costs, under insurance.
➡️ Elevating Patient Experience
Prioritizing patient satisfaction by improving the overall efficiency of the healthcare system.
Mechanics
To achieve its goals, NHCX operates on two main pillars:
1. Technical Specifications
Open Protocols for Data Exchange
NHCX uses open, secure protocols ensuring that health information is transferred safely and reliably. This includes advanced encryption methods and secure data transmission channels.Federated Deployment
Multiple NHCX instances can be deployed, which means that independent systems across different locations can be set up to handle health claims efficiently, securely, and in compliance with local regulations.Unique Identifier System
This helps in tracking each message exchange, ensuring accuracy and traceability.
2. Domain Specifications
Standardized Data Formats
Utilizing uniform data structures, such as FHIRV4, NHCX ensures that the information exchanged is consistent and interpretable across different systems.Comprehensive Data Models
These models cater to various aspects of healthcare claims, including patient details, service descriptions, and billing information.
But How Does It Work?
The following system architecture diagram visualizes the major functions of the system and the relationships between its various components. Let’s break it down to understand the functioning of NHCX.
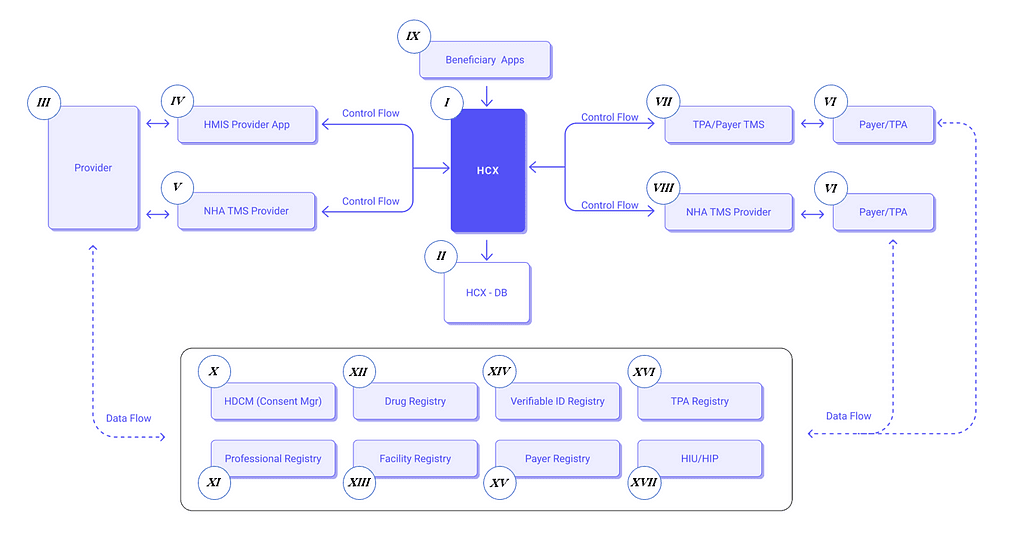
‘Control Flow’ indicates the direction of commands and controls being sent from the apps to the HCX and vice versa, while the dashed lines of ‘Data Flow’ signify the exchange of actual claims data that flows between the HCX and external entities such as HIU/HIP (Source for image: ABDM — NHCX)
Central Component
I. HCX (Health Claims Exchange)
This is the core system that facilitates all interactions between the different entities. It acts as the central hub for processing and routing the claims data.
II. HCX-DB
This represents the database associated with the HCX, where all transactional data related to health claims are stored and managed.
Providers
III. Provider
These are healthcare service providers, like hospitals and clinics.
IV. HMIS Provider App
Health Management Information System (HMIS) applications used by providers to manage patient information and services.
V. NHA TMS Provider
This is a Transaction Management System provided by NHA (National Health Authority) for providers to handle transactions and claims.
Payers/TPAs
VI. Payer/TPA
These are the entities like insurance companies (payers) or Third-Party Administrators (TPAs) that handle the management of claims.
VII. TPA/Payer TMS
Similar to the provider’s TMS, this system manages transaction and claims processes for payers or TPAs.
VIII. NHA TMS Payer/TPA
This represents the National Health Authority’s Transaction Management System used by payers or TPAs.
Beneficiaries
IX. Beneficiary Apps
Applications used by the beneficiaries, likely patients or insurance subscribers, to interact with the HCX for claims and other health-related services.
Registries
Below the central components, there are several registries that serve as authoritative sources for various types of data:
X. HDCM (Consent Mgr)
Health Data Consent Manager, which handles the consents for sharing personal health information in accordance with privacy laws and regulations.
XI. Professional Registry
A comprehensive listing of healthcare professionals including their credentials and specializations.
XII. Drug Registry
A database of medications that standardizes drug-related information.
XIII. Facility Registry
A list of healthcare facilities, potentially including their services, capacities, and other relevant details.
XIV. Verifiable ID Registry
This is used to verify the identities of individuals within the system.
XV. Payer Registry
A listing of insurance providers (payers) and their respective plans and services.
XVI. TPA Registry
A list of Third-Party Administrators who manage health claims and insurance policies.
XVII. HIU/HIP
Health Information User/Provider systems that may interact with the HCX for accessing or providing health information.
Overall Function
The architecture illustrates how the HCX serves as an intermediary that standardizes the communication between various healthcare stakeholders. It ensures that data exchange follows predefined protocols for security, privacy, and efficiency. The HCX processes claims, handles consent management through HDCM, and interacts with various registries to validate and cross-reference necessary information.
By using apps connected to HCX, providers and payers can submit and manage claims, while beneficiaries can track the status of their claims. All interactions with the HCX are governed by control flows ensuring proper command and data exchange, while the HCX-DB serves as the data repository for these transactions.
This infrastructure is designed to make the health claims process smoother, more transparent, and accessible, enhancing the efficiency of healthcare services delivery.
Benefits of NHCX
➡️ Efficiency in Claims Processing
With standardized and automated processes, NHCX cuts down the time for claim settlements significantly.
➡️ Greater Transparency
The rule-based mechanisms within NHCX enhance the trust and transparency between all parties.
➡️ Robust Data Security
The system’s focus on data security and privacy protects sensitive patient information.
➡️ Inclusivity in Healthcare
By enabling smaller healthcare providers to partake in cashless claim processes, NHCX democratizes access to healthcare services.
➡️ Stakeholder Engagement
NHCX is a collaborative effort involving:
→ Healthcare Providers
Who can now manage claims more effectively.
→ Insurers
Who benefit from a streamlined, accurate claims processing system.
→ Patients
Who experience inclusion of Out Patient Department (OPD) services, expedited pre-authorization, and reduced discharges times.
HealthCRED and The Road Ahead
The future of NHCX is bright. As it gets more integrated into the healthcare system, we can expect a significant reduction in administrative overheads, a boost in the efficiency of healthcare delivery, and an overall improvement in patient care and experience.
By demystifying its workings, we hope to have illuminated how NHCX is pathbreaking for patients, healthcare providers, and financiers alike. Whether you’re a medical professional seeking streamlined financial solutions, a patient navigating the complexities of healthcare financing, or an investor looking to contribute to this vital sector, NHCX offers a pathway towards more efficient, accessible, and sustainable healthcare financing.
We at HealthCRED are committed to empowering our partners through such innovative platforms, and we invite you to reach out to us to explore how NHCX can transform your healthcare experience and financial journey.